HP ssacli commands in ESXi:
https://itbru.ru/index.php/2019/09/04/hp-ssacli-commands/
https://be-virtual.net/hpe-storage-controller-management-ssacli/
https://support.hpe.com/hpesc/public/docDisplay?docId=emr_na-a00018717en_us
https://kb.gtkc.net/hp-smart-array-cli-commands/
https://wiki.froberg.org/en/hpe-storage-controller-management-ssacli
Invoke SSACLI command from remote server: esxcli –server=”servername or IP” –user=”username” –password=”root password” ssacli cmd -q “controller all show status”
HPE SSACLI – Abréviation
All commands have a short name to reduce the length of the total input provided to the ssacli tool:
### Shortnames:
– chassisname = ch
– controller = ctrl
– logicaldrive = ld
– physicaldrive = pd
– drivewritecache = dwc
– licensekey = lk
### Specify drives:
– A range of drives (one to three): 1E:1:1-1E:1:3
– Drives that are unassigned: allunassigned
HPE SSACLI – Status
To view the status of the controller, disks or volumes you can run all sorts of commands to get information about what is going on in your VMware ESXi server. The extensive detail is very useful for troubleshooting and gathering information about the system.
# Show – Controller Slot 1 Controller configuration basic
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 show config
# Show – Controller Slot 1 Controller configuration detailed
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 show detail
# Show – Controller Slot 1 full configuration
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 show config detail
# Show – Controller Slot 1 Status
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 show status
# Show – All Controllers Configuration
./ssacli ctrl all show config
# Show – Controller slot 1 logical drive 1 status
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 ld 1 show status
# Show – Physical Disks status basic
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 pd all show status
# Show – Physical Disk status detailed
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 pd all show status
# Show – Logical Disk status basic
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 ld all show status
# Show – Logical Disk status detailed
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 ld all show detail
HPE SSACLI – Creating
Creating a new logical drive can be done online with the HPE Smart Array controllers. I have displayed some basic examples.
# Create – New single disk volume
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 create type=ld drives=2I:0:8 raid=0 forced
# Create – New spare disk (two defined)
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 array all add spares=2I:1:6,2I:1:7
# Create – New RAID 1 volume
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 create type=ld drives=1I:0:1,1I:0:2 raid=1 forced
# Create – New RAID 5 volume
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 create type=ld drives=1I:0:1,1I:0:2,1I:0:3 raid=5 forced
HPE SSACLI – Adding drives to logical drive
Adding drives to an already created logical drive is possible with the following commands. You need to perform two actions: adding the drive(s) and expanding the logical drive. Keep in mind: make a backup before performing the procedure.
# Add – All unassigned drives to logical drive 1
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 ld 1 add drives=allunassigned
# Modify – Extend logical drive 2 size to maximum (must be run with the “forced” flag)
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 ld 2 modify size=max forced
HPE SSACLI – Rescan controller
To issue a controller rescan, you can run the following command. This can be interesting for when you add new drives in hot swap bays.
### Rescan all controllers
./ssacli rescan
HPE SSACLI – Drive Led Status
The LED status of the drives can also be controlled by the ssacli utility. An example is displayed below how to enable and disable a LED.
# Led – Activate LEDs on logical drive 2 disks
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 ld 2 modify led=on
# Led – Deactivate LEDs on logical drive 2 disks
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 ld 2 modify led=off
# Led – Activate LED on physical drive
./ssacli ctrl slot=0 pd 1I:0:1 modify led=on
# Led – Deactivate LED on physical drive
./ssacli ctrl slot=0 pd 1I:0:1 modify led=off
HPE SSACLI – Modify Cache Ratio
Modify the cache ratio on a running system can be interesting for troubleshooting and performance beanchmarking.
# Show – Cache Ratio Status
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 modify cacheratio=?
# Modify – Cache Ratio read: 25% / write: 75%
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 modify cacheratio=25/75
# Modify – Cache Ratio read: 50% / write: 50%
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 modify cacheratio=50/50
# Modify – Cache Ratio read: 0% / Write: 100%
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 modify cacheratio=0/100
HPE SSACLI – Modify Write Cache
Changing the write cache settings on the storage controller can be done with the following commands:
# Show – Write Cache Status
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 modify dwc=?
# Modify – Enable Write Cache on controller
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 modify dwc=enable forced
# Modify – Disable Write Cache on controller
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 modify dwc=disable forced
# Show – Write Cache Logicaldrive Status
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 logicaldrive 1 modify aa=?
# Modify – Enable Write Cache on Logicaldrive 1
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 logicaldrive 1 modify aa=enable
# Modify – Disable Write Cache on Logicaldrive 1
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 logicaldrive 1 modify aa=disable
HPE SSACLI – Modify Rebuild Priority
Viewing or changing the rebuild priority can be done on the fly. Even when the rebuild is already active. Used it myself a couple of times to lower the impact on production.
# Show – Rebuild Priority Status
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 modify rp=?
# Modify – Set rebuildpriority to Low
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 modify rebuildpriority=low
# Modify – Set rebuildpriority to Medium
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 modify rebuildpriority=medium
# Modify – Set rebuildpriority to High
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 modify rebuildpriority=high
HPE SSACLI – Modify SSD Smart Path
You can modify the HPE SDD Smart Path feature by disabling or enabling. To make clear what the HPE SDD Smart Path includes, here is a official statement by HPE:
“HP SmartCache feature is a controller-based read and write caching solution that caches the most frequently accessed data (“hot” data) onto lower latency SSDs to dynamically accelerate application workloads. This can be implemented on direct-attached storage and SAN storage.”
For example, when running VMware vSAN SSD Smart Path must be disabled for better performance. In some cases worse the entire vSAN disk group fails.
# Note: This command requires the array naming type like A/B/C/D/E
# Modify – Enable SSD Smart Path
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 array a modify ssdsmartpath=enable
# Modify – Disable SSD Smart Path
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 array a modify ssdsmartpath=disable
HPE SSACLI – Delete Logical Drive
Deleting a logical drive on the HPE Smart Array controller can be done with the following commands.
# Delete – Logical Drive 1
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 ld 1 delete
# Delete – Logical Drive 2
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 ld 2 delete
HPE SSACLI – Erasing Physical Drives
In some cases, you need to erase a physical drive. This can be performed with multiple erasing options. Also, you can stop the process.
Erase patterns available:
Default
Zero
Random_zero
Random_random_zero
# Erase physical drive with default erasepattern
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 pd 2I:1:1 modify erase
# Erase physical drive with zero erasepattern
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 pd 2I:1:1 modify erase erasepattern=zero
# Erase physical drive with random zero erasepattern
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 pd 1E:1:1-1E:1:3 modify erase erasepattern=random_zero
# Erase physical drive with random random zero erasepattern
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 pd 1E:1:1-1E:1:3 modify erase erasepattern=random_random_zero
# Stop the erasing process on phsyical drive 1E:1:1
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 pd 1E:1:1 modify stoperase
HPE SSACLI – License key
In some cases a licence key needs to be installed on the SmartArray storage controller to enable the advanced features. This can be done with the following command:
# License key installation
./ssacli ctrl slot=1 licensekey XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX
# License key removal
./ssacli ctrl slot=5 lk XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX delete
HP RAID Controller monitoring statuses:
If you have logical drive status: “The logical drive is queued for rebuilding” or “Status: Ready for Rebuild” after replacing a failed HDD disk, and you can’t make controller to start rebuilding, than:
1) probably the disk you’ve just replaced is not completely identical as other disks in the RAID group.
2) you hafe “phantom” disk, whose error you can see only in ADUReport.
HP printers repair:
http://www.startcopy.ru/repair/repair.shtml
HP RAID controller user manual, very useful for understanding RAID levels risks:
And IBM manual for more information:
https://www.ibm.com/docs/sl/psfa/1.6?topic=requirements-raid-implementation-considerations
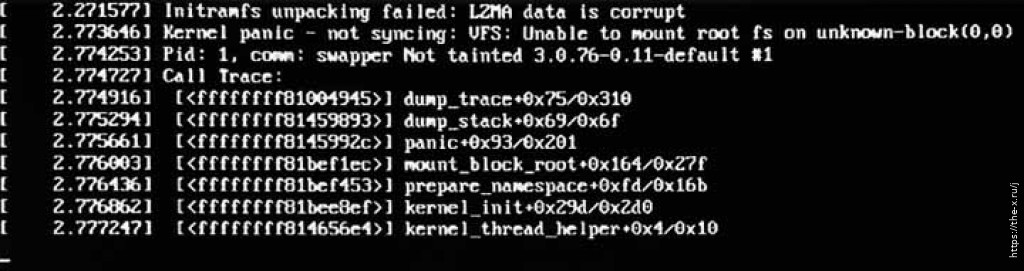
HP Smart Storage Administration (HP SSA) fails to load while started from server’s POST with “LZMA data is corrupt” error:
After almost a half year of standing powered down my HP Microserver Gen 8 with Smart Array P222 RAID controller installed in the server’s PCI-E slot showed an error when I’ve tried to enter the HP SSA from the POST screen:
I’ve tried to load the SSA from ISO through iLO and it’s worked fine. The SSA was able to see the controller, disks, logical drives, cache etc.
At the beginning I thought that the server’s “internal” SSA is sitting inside one of the RAID controller’s chips. So I’ve found and flashed a latest firmware for the controller 8.32(E). It didn’t helped.
Than I saw that squashfs.img from the SSA Offline ISO (ssaoffline-3.40-3.0.iso) is an image with some Linux OS containing SSA software and it’s size of almost 300 MB is more than 10 times larger than entire controller’s firmware. That means that internal SSA firmware sits on some of the chips located on the server’s motherboard.
That thoughts was approved after searching “LZMA data is corrupt Smart Storage Administrator“:
https://community.hpe.com/t5/proliant-servers-ml-dl-sl/dl-380-g9-ssa-error/td-p/7066716
https://community.hpe.com/t5/proliant-servers-ml-dl-sl/p420-controller-menu-crashing-after-trying-to-load/td-p/7019834
I’ve loaded the Intelligent-Provisioning-Recovery-Media-1.74-IP174.2021_0707.4.iso and it has rewrited the updated Intelligent Provosioning and Smart Storage Administration software on the Microserver’s NAND.
Interestingly that Gen 9’s recovery image Intelligent-Provisioning-for-Gen9-Servers-2.87.iso is detecting the server as Gen 8 and successfully updating the IP and SSA software, but SSA don’t see the P222 controller then.
Reset iLo password from ESXi console:
Old way:
https://vcloudnine.de/reset-the-hp-ilo-administrator-password-with-hponcfg-on-esxi/
Works only with HPE ESXi image before HPE VMWare Esxi vSphere 7.0 U3 Build 20036589 Release October 2022
https://support.hpe.com/hpesc/public/docDisplay?docId=sf000091060en_us&docLocale=en_US
New way of resetting of password using iLOrest:
https://developer.hpe.com/blog/how-to-change-the-factory-generated-ilo-administrator-password/
https://www.it-react.com/index.php/2022/04/23/reset-or-configure-hp-ilo-directly-from-esxi-host/